RocketMQ源码解析-Broker故障恢复
以下源码基于Rocket MQ 4.7.0
RocketMQ正常退出或者异常退出的时候,如果重新启动那么怎么恢复数据。接下来通过代码来分析这个过程。
1.Broker故障恢复
在broker第一次启动或者重新启动的时候会调用这样的一段代码:
//BrokerController#initialize 中的方法
public boolean initialize() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
result = result && this.messageStore.load();
}
从上面的代码可以知道,在broker进行初始的时候,会 MessageStore#load 方法,这个方法的默认实现为 DefaultMessageStore 。接下来看一下 load方法这里就是Broker恢复的入口:
public boolean load() {
boolean result = true;
try {
//通过判断abort文件是否存在来判断是否正常退出
boolean lastExitOK = !this.isTempFileExist();
if (null != scheduleMessageService) {
//解析延迟的等级-可以自己配置
result = result && this.scheduleMessageService.load();
}
// 加载CommitLog
result = result && this.commitLog.load();
//加载ConsumeQueue
result = result && this.loadConsumeQueue();
if (result) {
this.storeCheckpoint =
new StoreCheckpoint(StorePathConfigHelper.getStoreCheckpoint(this.messageStoreConfig.getStorePathRootDir()));
this.indexService.load(lastExitOK);
//恢复入口
this.recover(lastExitOK);
this.getMaxPhyOffset());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
result = false;
}
if (!result) {
this.allocateMappedFileService.shutdown();
}
return result;
}
通过上面的代码可以知道恢复是通过 recover 方法来处理。
private void recover(final boolean lastExitOK) {
//获取ConsumeQueue最大的物理偏移量--这个也是CommitLog中物理偏移量(后续会有测试的打印代码)
long maxPhyOffsetOfConsumeQueue = this.recoverConsumeQueue();
if (lastExitOK) {
//正常退出处理
this.commitLog.recoverNormally(maxPhyOffsetOfConsumeQueue);
} else {
//异常退出处理
this.commitLog.recoverAbnormally(maxPhyOffsetOfConsumeQueue);
}
this.recoverTopicQueueTable();
}
在RocketMQ的4.7.0版本中CommitLog#recoverAbnormally方法显示为过期,这里暂时就不去分析这个情况。等后续看这里如何处理。
2.CommitLog和ConsumeQueue的恢复
下面来通过添加测试代码的方式说明一下 maxPhyOffsetOfConsumeQueue 到底是什么值。首先能在 recover 中添加如下代码然后打包源码:

然后启动broker,我这里启动这个值为384
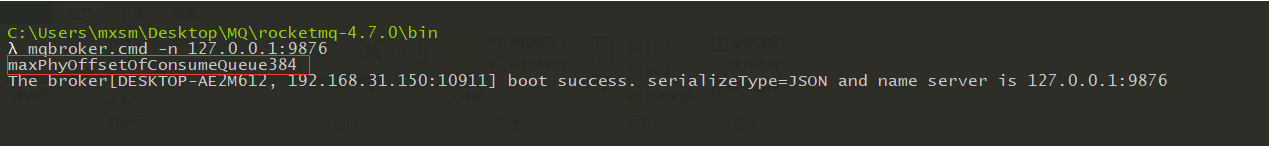
然后通过客户端在产生一条消息到Broker
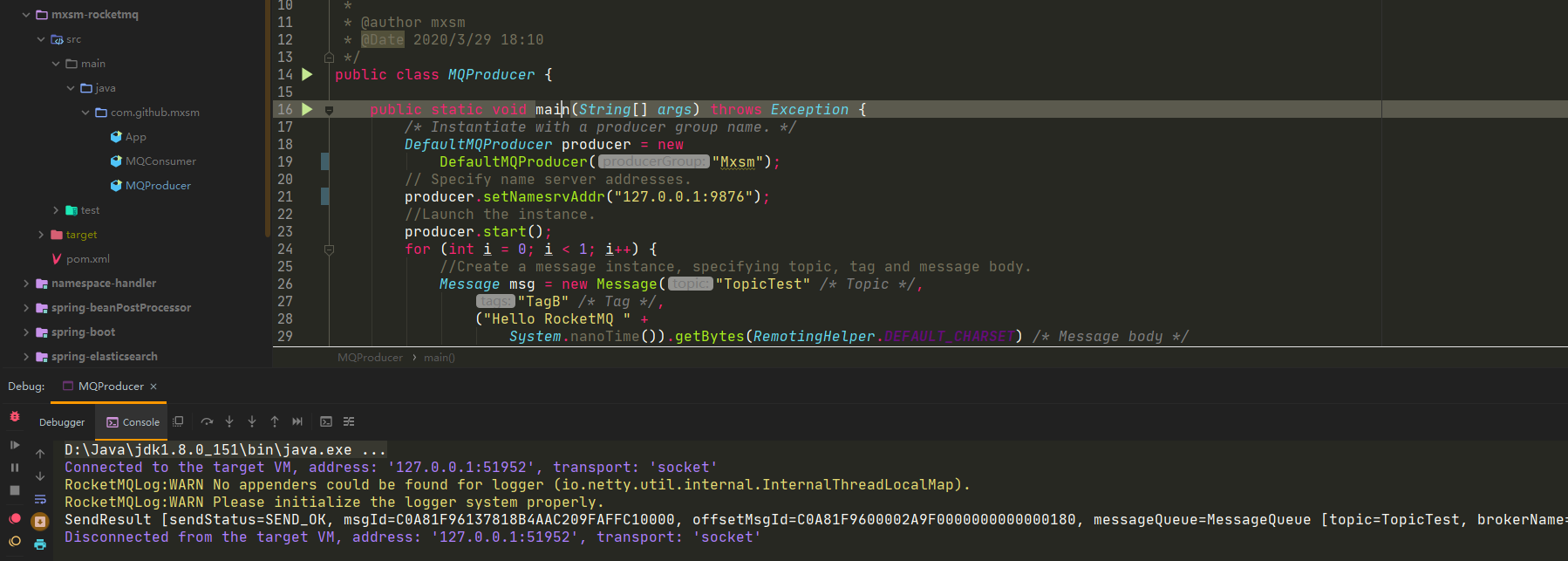
通过监控broker日志(这个也是自己添加的),存入CommitLog的大小为192字节。

然后重启Broker发现这个 maxPhyOffsetOfConsumeQueue 变为了 576 。
通过这个日志的打印说明了 maxPhyOffsetOfConsumeQueue 为CommitLog日志中的物理偏移量。接下来分一下 CommitLog#recoverNormally 是怎么样来处理的:
public void recoverNormally(long maxPhyOffsetOfConsumeQueue) {
//CRC检查在恢复的时候--默认值true
boolean checkCRCOnRecover = this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().isCheckCRCOnRecover();
//获取CommitLog的列表
final List<MappedFile> mappedFiles = this.mappedFileQueue.getMappedFiles();
//非空说明不是第一次启动
if (!mappedFiles.isEmpty()) {
// 大于三个CommitLog文件就从最新的三个开始,小于三个就有多少校验多少
int index = mappedFiles.size() - 3;
if (index < 0)
index = 0;
MappedFile mappedFile = mappedFiles.get(index);
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = mappedFile.sliceByteBuffer();
long processOffset = mappedFile.getFileFromOffset();
long mappedFileOffset = 0;
while (true) {
//每条数据的校验然后返回DispatchRequest
DispatchRequest dispatchRequest = this.checkMessageAndReturnSize(byteBuffer, checkCRCOnRecover);
int size = dispatchRequest.getMsgSize();
// 正常数据处理
if (dispatchRequest.isSuccess() && size > 0) {
mappedFileOffset += size;
}
//来到文件结尾或者处理完了,或者需要换文件
else if (dispatchRequest.isSuccess() && size == 0) {
index++;
//最新的三个文件都处理完了
if (index >= mappedFiles.size()) {
break;
} else {
//切换文件
mappedFile = mappedFiles.get(index);
byteBuffer = mappedFile.sliceByteBuffer();
processOffset = mappedFile.getFileFromOffset();
mappedFileOffset = 0;
}
}
// 终端文件的读取由于错误
else if (!dispatchRequest.isSuccess()) {
log.info("recover physics file end, " + mappedFile.getFileName());
break;
}
}
processOffset += mappedFileOffset;
//设置刷新位置
this.mappedFileQueue.setFlushedWhere(processOffset);
//设置接下来文件的提交位置
this.mappedFileQueue.setCommittedWhere(processOffset);
//删除过期的文件
this.mappedFileQueue.truncateDirtyFiles(processOffset);
//清除ConsumeQueue多余的数据
if (maxPhyOffsetOfConsumeQueue >= processOffset) {
this.defaultMessageStore.truncateDirtyLogicFiles(processOffset);
}
} else {
// CommitLog日志文件全部删除(特殊情况就是第一次启动)
this.mappedFileQueue.setFlushedWhere(0);
this.mappedFileQueue.setCommittedWhere(0);
this.defaultMessageStore.destroyLogics();
}
}
上面代码有一个两个变量可能不太明白他的数据到底为多少一个是 processOffset、mappedFileOffset 下面来通过添加日志打印的模式来看一下,首先如下图所示添加代码然后打包对应的模块:

然后启动Broker看一下对应的值如下图:
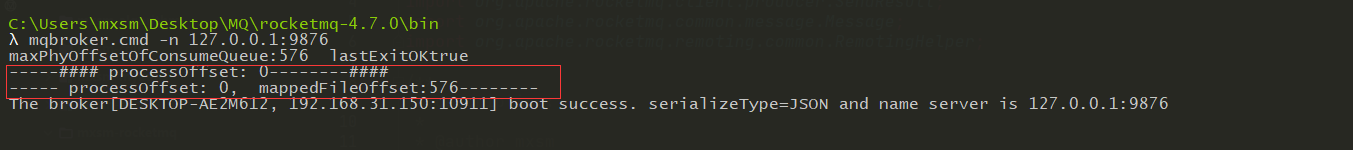
processOffset 启动的时候其实是0,mappedFileOffset 就是每一个CommitLog的处理数据。
上面主要分为两种正常恢复:
-
存在CommitLog日志文件- 检查最新三个文件数据中的每条数据
- 设置flushedWhere和committedWhere值
- 删除处理过了的CommitLog日志文件。
-
不存在CommitLog日志文件(第一次启动或者日志文件被删除)设置flushedWhere和committedWhere为0并且删除ConsumeQueue文件
3.TopicQueue的恢复
//topic queueId和offset的关系
public void recoverTopicQueueTable() {
HashMap<String/* topic-queueid */, Long/* offset */> table = new HashMap<String, Long>(1024);
long minPhyOffset = this.commitLog.getMinOffset();
for (ConcurrentMap<Integer, ConsumeQueue> maps : this.consumeQueueTable.values()) {
for (ConsumeQueue logic : maps.values()) {
String key = logic.getTopic() + "-" + logic.getQueueId();
table.put(key, logic.getMaxOffsetInQueue());
logic.correctMinOffset(minPhyOffset);
}
}
this.commitLog.setTopicQueueTable(table);
}
这个里面的关系数据会在CommitLog日志数据保存在如下代码中会用到。 DefaultAppendMessageCallback#doAppend 方法中。
Long queueOffset = CommitLog.this.topicQueueTable.get(key);
ueueOffset++;
CommitLog.this.topicQueueTable.put(key, queueOffset);