EventMesh GRPC protocol upgrade design
1. Background
The current data exchange of EventMesh's GRPC protocol uses EventMesh's custom SimpleMessage protocol. To better support the CloudEvents specification, the SimpleMessage protocol is being modified to use CloudEvents-provided Protobuf format protocol.
2. Architecture
SimpleMessage is mainly used for data exchange between the GRPC SDK and the runtime. A new EventMesh CloudEvent protocol (fully compatible with the CloudEvents specification) will be defined to replace SimpleMessage.
Tips: The Protobuf format in CloudEvents' current 1.0.2 release adds batch processing functionality, but the corresponding SDK has not yet provided batch processing implementation.
By replacing the SimpleMessage protocol with the redefined EventMesh CloudEvent protocol, it will better implement the CloudEvents specification.
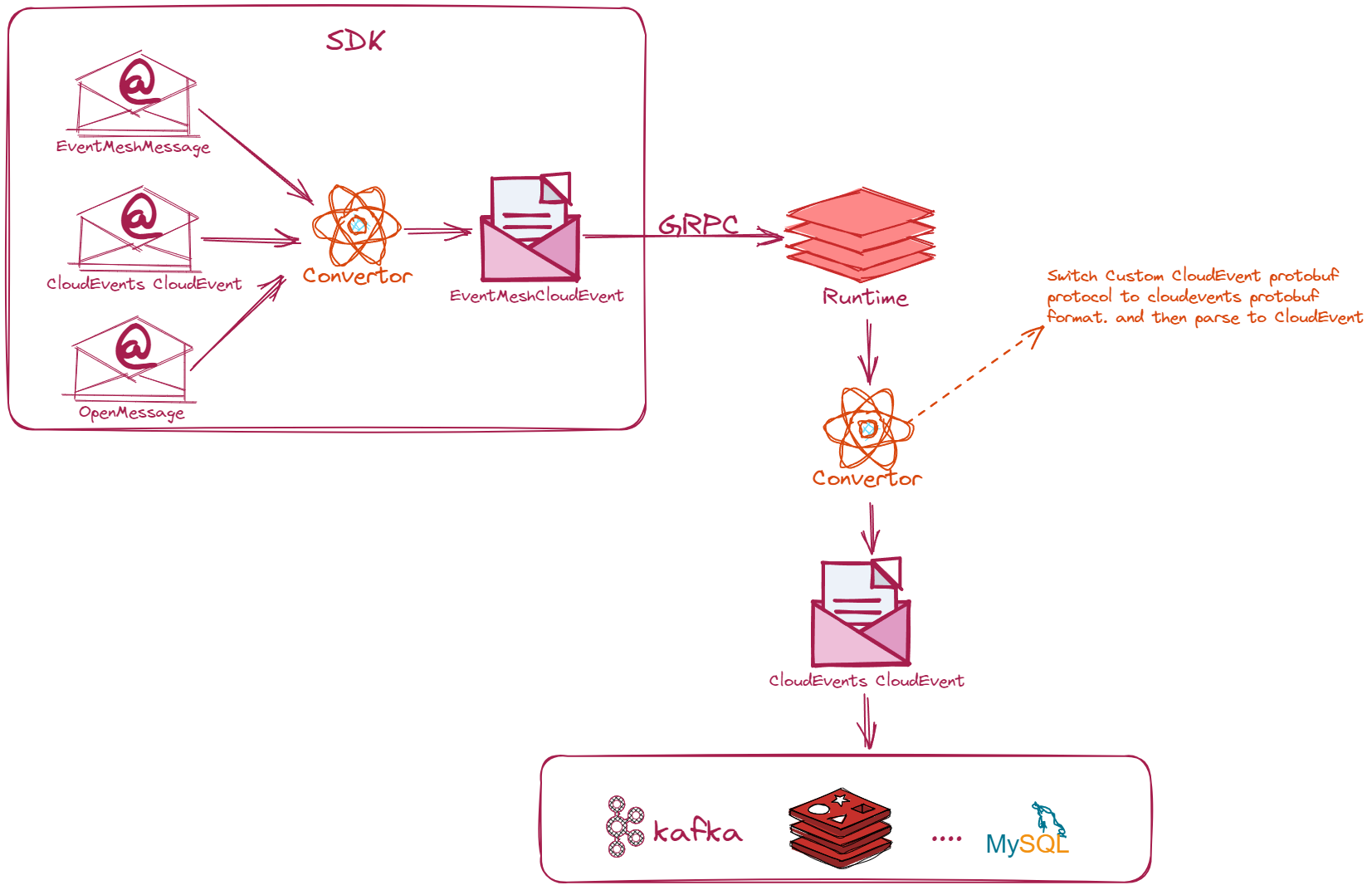
- The SDK sends three types of messages via GRPC: EventMeshMessage, CloudEvent (in compliance with the CloudEvents specification), and Openmessage. These three types of messages are converted into the data format of EventMesh's CloudEvent protobuf format through a converter.
- The three types of messages are converted into EventMesh's custom CloudEvent protobuf format through a converter, and transmitted during the GRPC call.
- After receiving the EventMesh custom CloudEvent protobuf format message sent by the SDK, the Runtime performs necessary validation on the message, including required values in compliance with the CloudEvents specification, as well as values that EventMesh needs to validate.
- Once the validation is successful, the data is converted into CloudEvent (in compliance with the CloudEvents specification) format for subsequent data processing.
Tips: The custom EventMesh CloudEvent protobuf format follows the same format specification as CloudEvents' Protobuf format.
3. How to transform
3.1 Transformation of data protocol
definition of data protocol:
syntax = "proto3";
package org.apache.eventmesh.cloudevents.v1;
import "google/protobuf/any.proto";
import "google/protobuf/timestamp.proto";
option java_package = "org.apache.eventmesh.common.protocol.grpc.cloudevents";
option java_multiple_files = true;
option java_outer_classname = "EventMeshCloudEvents";
message CloudEvent {
// -- CloudEvent Context Attributes
// Required Attributes
string id = 1;
string source = 2; // URI-reference
string spec_version = 3;
string type = 4;
// Optional & Extension Attributes
map<string, CloudEventAttributeValue> attributes = 5;
// -- CloudEvent Data (Bytes, Text, or Proto)
oneof data {
bytes binary_data = 6;
string text_data = 7;
google.protobuf.Any proto_data = 8;
}
/**
* The CloudEvent specification defines
* seven attribute value types...
*/
message CloudEventAttributeValue {
oneof attr {
bool ce_boolean = 1;
int32 ce_integer = 2;
string ce_string = 3;
bytes ce_bytes = 4;
string ce_uri = 5;
string ce_uri_ref = 6;
google.protobuf.Timestamp ce_timestamp = 7;
}
}
}
/**
* CloudEvent Protobuf Batch Format
*
*/
message CloudEventBatch {
repeated CloudEvent events = 1;
}
The defined data protocol is completely identical to the CloudEvents 1.0.2 specification.
3.2 Service protocol transformation
syntax = "proto3";
package org.apache.eventmesh.cloudevents.v1;
import "google/protobuf/empty.proto";
import "eventmesh-cloudevents.proto";
option java_package = "org.apache.eventmesh.common.protocol.grpc.cloudevents";
option java_multiple_files = true;
option java_outer_classname = "EventMeshGrpcService";
service PublisherService {
//publish event
rpc publish(CloudEvent) returns (CloudEvent);
//publish event with reply
rpc publishReply(CloudEvent) returns (CloudEvent);
//publish event one way
rpc publishOneWay(CloudEvent) returns (google.protobuf.Empty);
// publish batch event
rpc batchPublish(CloudEventBatch) returns (CloudEvent);
//publish batch event one way
rpc batchPublishOneWay(CloudEventBatch) returns (google.protobuf.Empty);
}
service ConsumerService {
// The subscribed event will be delivered by invoking the webhook url in the Subscription
rpc subscribe(CloudEvent) returns (CloudEvent);
// The subscribed event will be delivered through stream of Message
rpc subscribeStream(stream CloudEvent) returns (stream CloudEvent);
rpc unsubscribe(CloudEvent) returns (CloudEvent);
}
service HeartbeatService {
rpc heartbeat(CloudEvent) returns (CloudEvent);
}
3.3 SDK upgrade and transformation
- The SDK's external interfaces EventMeshGrpcProducer and EventMeshGrpcConsumer do not need to be modified (including publishing and subscribing), only a converter needs to be added to convert the three types of messages, EventMeshMessage, CloudEvent (according to CloudEvents specifications), and Openmessage, into the custom CloudEvent Protobuf format.
- Due to the changes in the parameters of the Grpc service, corresponding changes need to be made to the SDK's Sub for Grpc.
3.4 Runtime GRPC upgrade and transformation
-
Refactor the entire publishing and subscribing processing logic, add unified data verification and permission verification, as well as data processing, including the following processing classes:
- ProducerService: Processes publishing requests.
- ConsumerService: Processes consuming requests.
- HeartbeatService: Processes heartbeat requests.
The data verification and permission verification are processed uniformly.
-
Add a converter to convert EventMesh's CloudEvent Protobuf protocol data into CloudEvents-compliant data.
4. Compatibility issues
- Using the custom CloudEvent protocol can be compatible with the standard protocol of CloudEvents very well.
- EventMesh has no data compatibility issues when upgrading from a lower version to a higher version.