Java NIO 知识梳理和例子
1. 核心组件
读写在Java NIO中的最基本操作,可以创建Buffer然后从Channel中读取数据,同时也可以往Channel中写入数据。
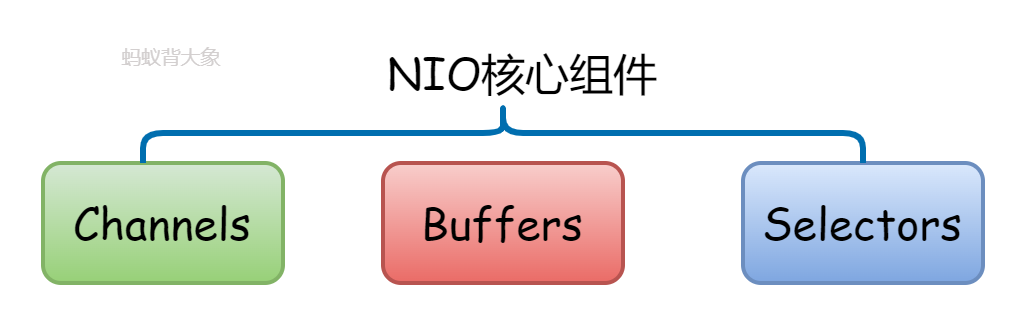
- Channels
- Buffers
- Selectors
在NIO中,我们使用通道和缓冲区。NIO中的所有I/O都是从一个通道开始的。数据总是从缓冲区写入到通道,从通道读取到缓冲区
2. Channels
Channel 在 java.nio.channels 包下面,下面来看一下继承关系:
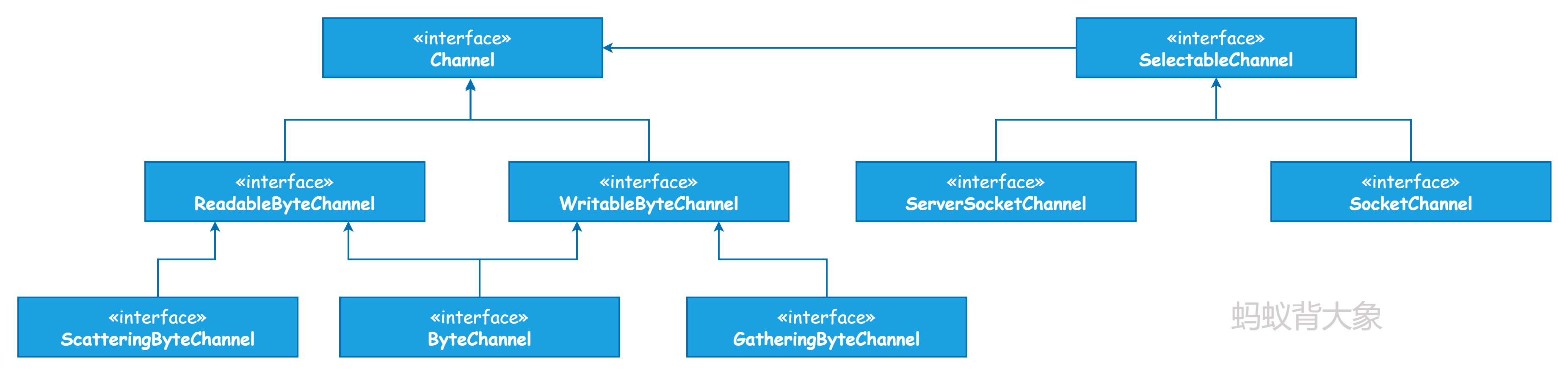
2.1 SocketChannel
SocketChannel被用于TCP网络通信链接一个Channel,两种创建SocketChannel的方法:
- 当有连接到达ServerSocketChannel的时候
- 打开SocketChannel并且连接服务
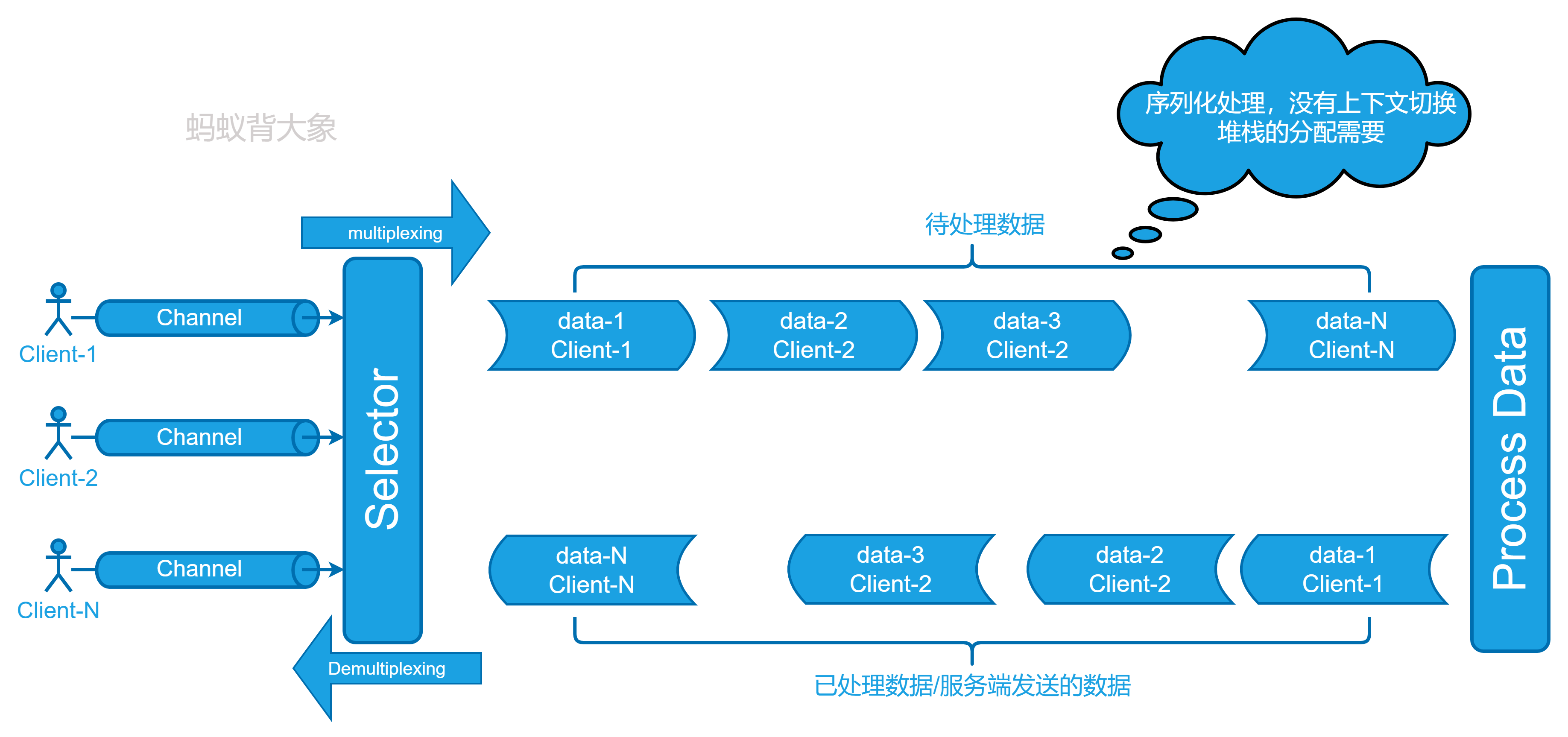
让我们看看使用Selector的SocketChannel客户端-服务器通信框架图:
2.2 SocketChannel的操作
打开SocketChannel:
SocketChannel sc = SocketChannel.open();
sc.connect(new InetSocketAddress("http://localhost", 8080));
从SocketChannel读取数据:
ByteBuffer bb = ByteBuffer.allocate(84);
int bytesRead = sc.read(bb);
往SocketChannel写入数据:
String newData = "The new String is writing in a file ..." + System.currentTimeMillis();
ByteBuffer bb= ByteBuffer.allocate(48);
bb.clear();
bb.put(newData.getBytes());
bb.flip();
while(bb.hasRemaining()) {
sc.write(bb);
}
关闭SocketChannel:
sc.close();
2.3 ServerSocketChannel
ServerSocketChanne被用于TCP网络通信链接一个Channel,但是主要用于服务端
2.4 ServerSocketChannel操作
打开ServerSocketChannel:
ServerSocketChannel sc = ServerSocketChannel.open();
sc.connect(new InetSocketAddress("http://localhost", 8080));
监听端口进来的链接:
while(true){
SocketChannel sc = serverSocketChannel.accept();
}
Tips: 当有连接接入监听返回SocketChannel
从ServerSocketChannel读数据:
ByteBuffer bb = ByteBuffer.allocate(84);
int bytesRead = sc.read(bb);
往ServerSocketChannel写数据:
String newData = "The new String is writing in a file ..." + System.currentTimeMillis();
ByteBuffer bb= ByteBuffer.allocate(48);
bb.clear();
bb.put(newData.getBytes());
bb.flip();
while(bb.hasRemaining()) {
sc.write(bb);
}
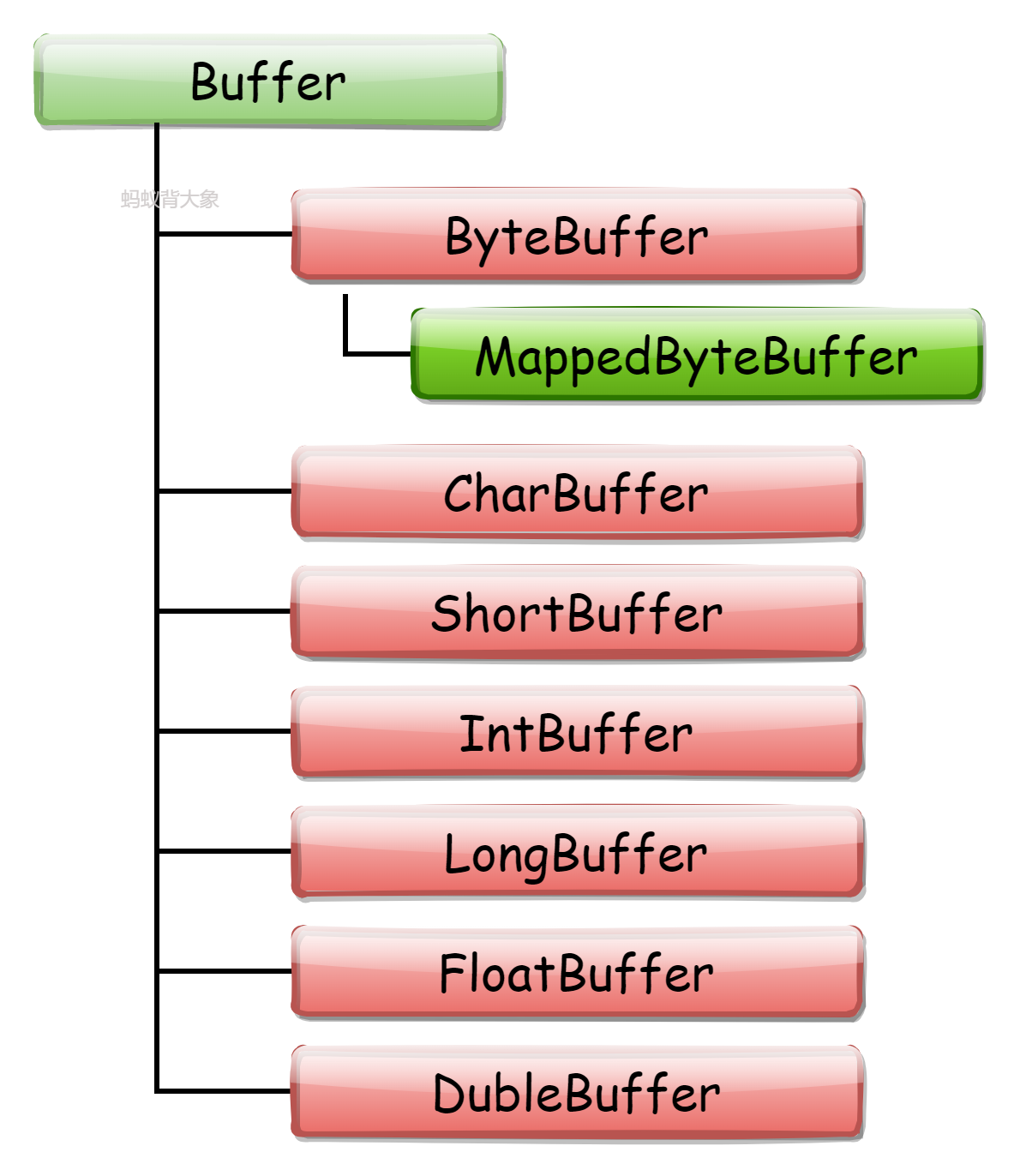
3. Buffers
下面看一下Buffer的继承关系:
4. Selectors
Selector用于使用单个线程处理多个通道。 因此,它需要更少的线程来处理通道。 对于操作系统来说,线程之间的切换开销很大。 因此,为了提高系统的效率
一个Selector处理多个Channel。
4.1 创建Selector
Selector selector = Selector.open();
4.2 创建ServerSocketChannel
ServerSocketChannel serverSocket = ServerSocketChannel.open();
InetSocketAddress hostAddress = new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080);
serverSocket.bind(hostAddress);
4.3 使用Selector选择Channel
在用选择器注册一个或多个通道时,我们可以调用select()方法之一。这个方法返回一个通道,该通道为我们想要执行的事件准备好了,例如 connect, read, write , accept。select方法有:
- int select(): select()方法返回的整数值告知有多少Channel准备好进行通信。
- int select(long TS): 和select()相同,除了它在最大TS(毫秒)时间段内阻塞
- int selectNow(): 非阻塞,返回任何准备好的通道
一旦调用了任何一个select()方法,返回了值。然后通过调用Selector的selectedkeys()获取到selected key 集合:
Set<SelectionKey> selectedKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
例子:
Set<SelectionKey> selectedKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> keyIterator = selectedKeys.iterator();
while(keyIterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = keyIterator.next();
if(key.isConnectable()) {
// The connection was established with a remote server.
} else if (key.isAcceptable()) {
// The connection was accepted by a ServerSocketChannel.
} else if (key.isWritable()) {
// The channel is ready for writing
} else if (key.isReadable()) {
// The channel is ready for reading
}
keyIterator.remove();
}
完整的选择环路框图如下所示:
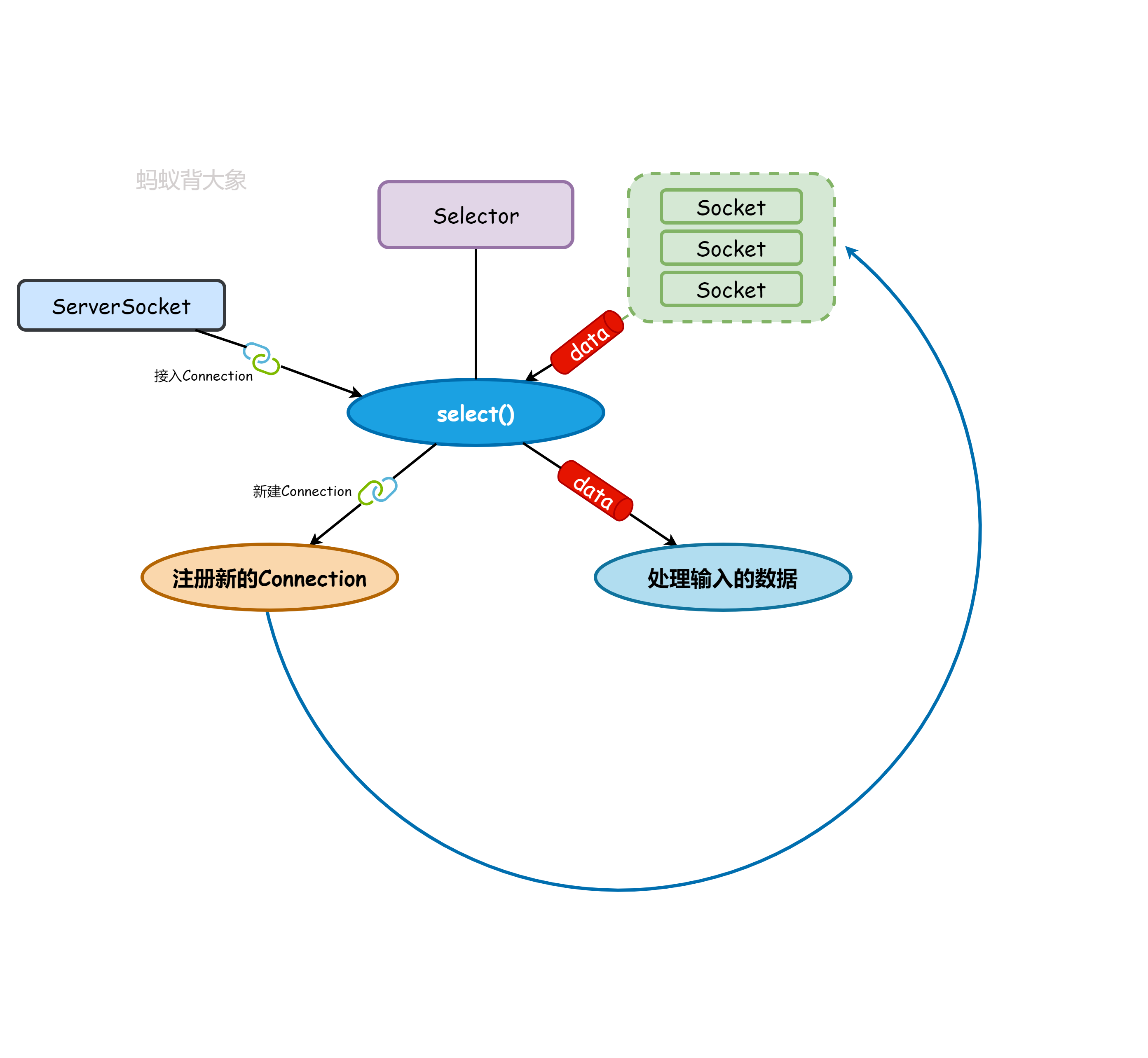
4.4 使用案例
服务端代码:
package com.github.mxsm.nio;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* @author mxsm
* @date 2022/3/10 23:26
* @Since 1.0.0
*/
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Selector selector = Selector.open();
ServerSocketChannel ssc = ServerSocketChannel.open();
InetSocketAddress hostAddress = new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080);
ssc.bind(hostAddress);
ssc.configureBlocking(false);
int ops = ssc.validOps();
SelectionKey selectKy = ssc.register(selector, ops, null);
for (;;) {
int noOfKeys = selector.select();
if(noOfKeys <= 0){
continue;
}
Set selectedKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator itr = selectedKeys.iterator();
while (itr.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey ky = (SelectionKey) itr.next();
if (ky.isAcceptable()) {
SocketChannel client = ssc.accept();
client.configureBlocking(false);
client.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
else if (ky.isReadable()) {
SocketChannel client = (SocketChannel) ky.channel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(256);
client.read(buffer);
String output = new String(buffer.array()).trim();
System.out.println("接收客户端信息: " + output);
ByteBuffer byteBuffer1 = ByteBuffer.wrap(("时间戳:"+System.currentTimeMillis()).getBytes(
StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
client.write(byteBuffer1);
}
itr.remove();
}
}
}
}
客户端代码:
package com.github.mxsm.nio;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* @author mxsm
* @date 2022/3/10 23:30
* @Since 1.0.0
*/
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
InetSocketAddress hA = new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080);
SocketChannel client = SocketChannel.open(hA);
System.out.println("The Client is sending messages to server...");
for (;;) {
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(("客户端时间戳:"+System.currentTimeMillis()).getBytes(
StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
client.write(buffer);
buffer.clear();
ByteBuffer buffer1 = buffer.allocate(256);
client.read(buffer1);
System.out.println("接收服务器消息:"+new String(buffer1.array(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8).trim());
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
}
}
}
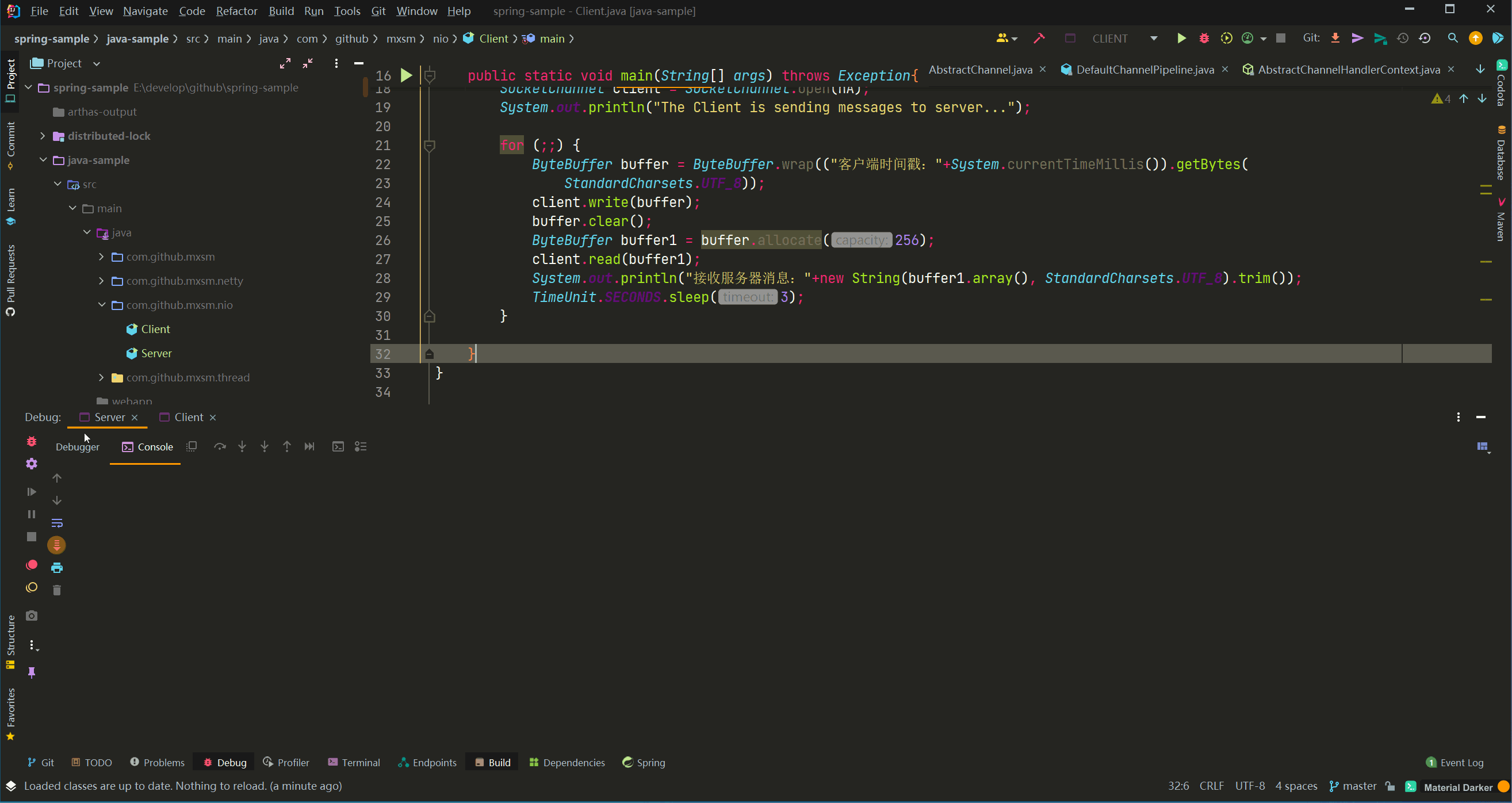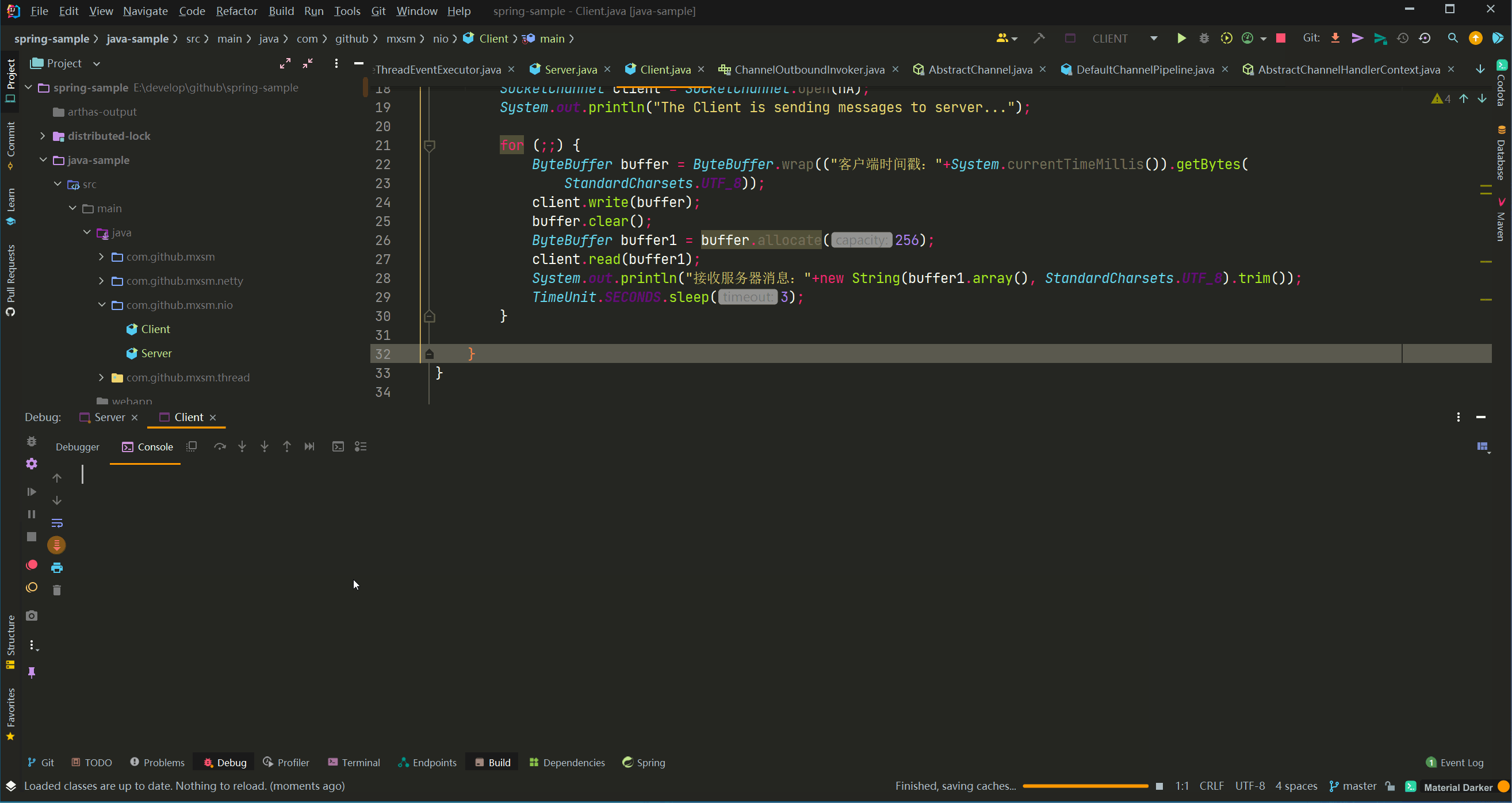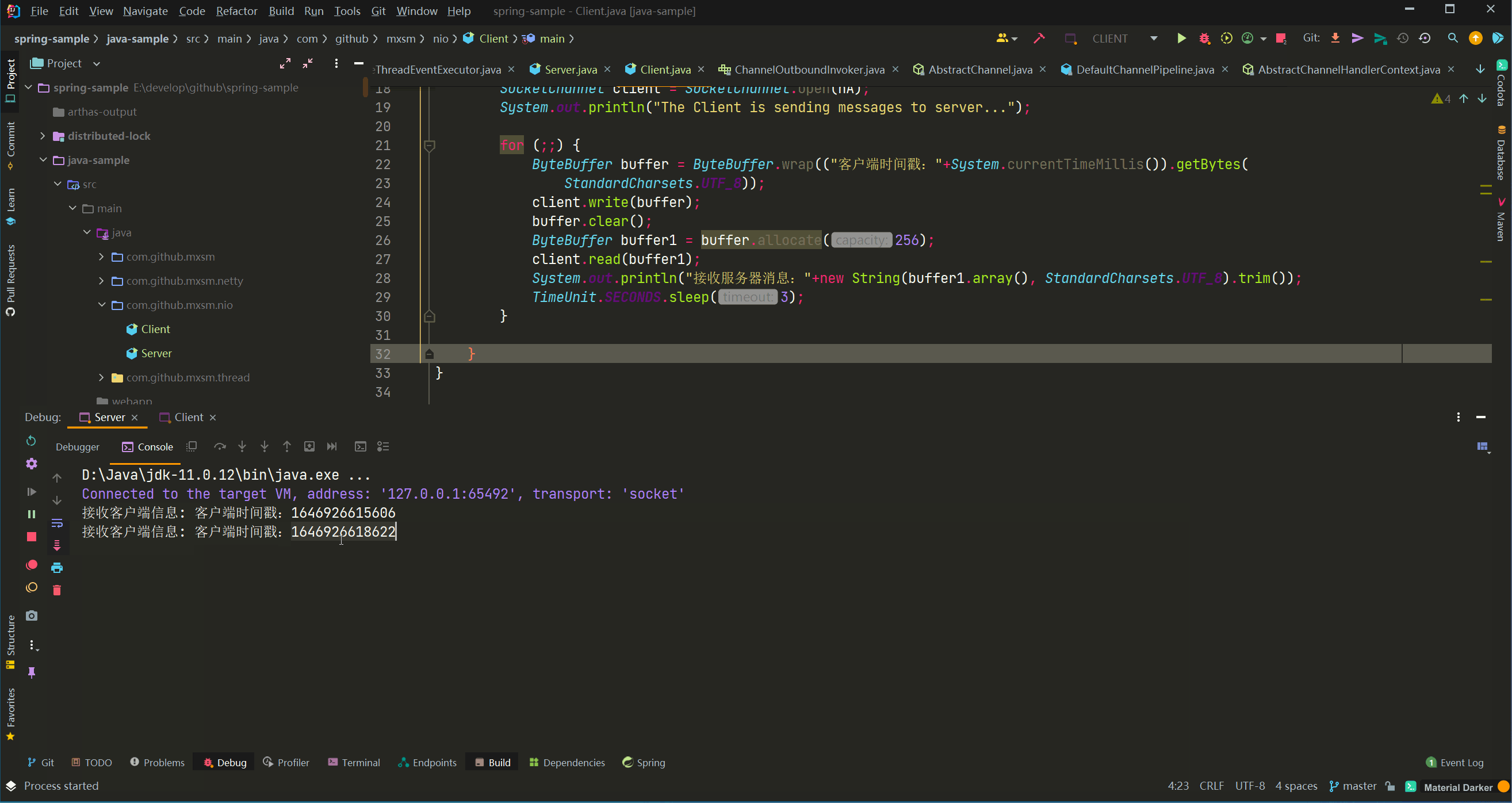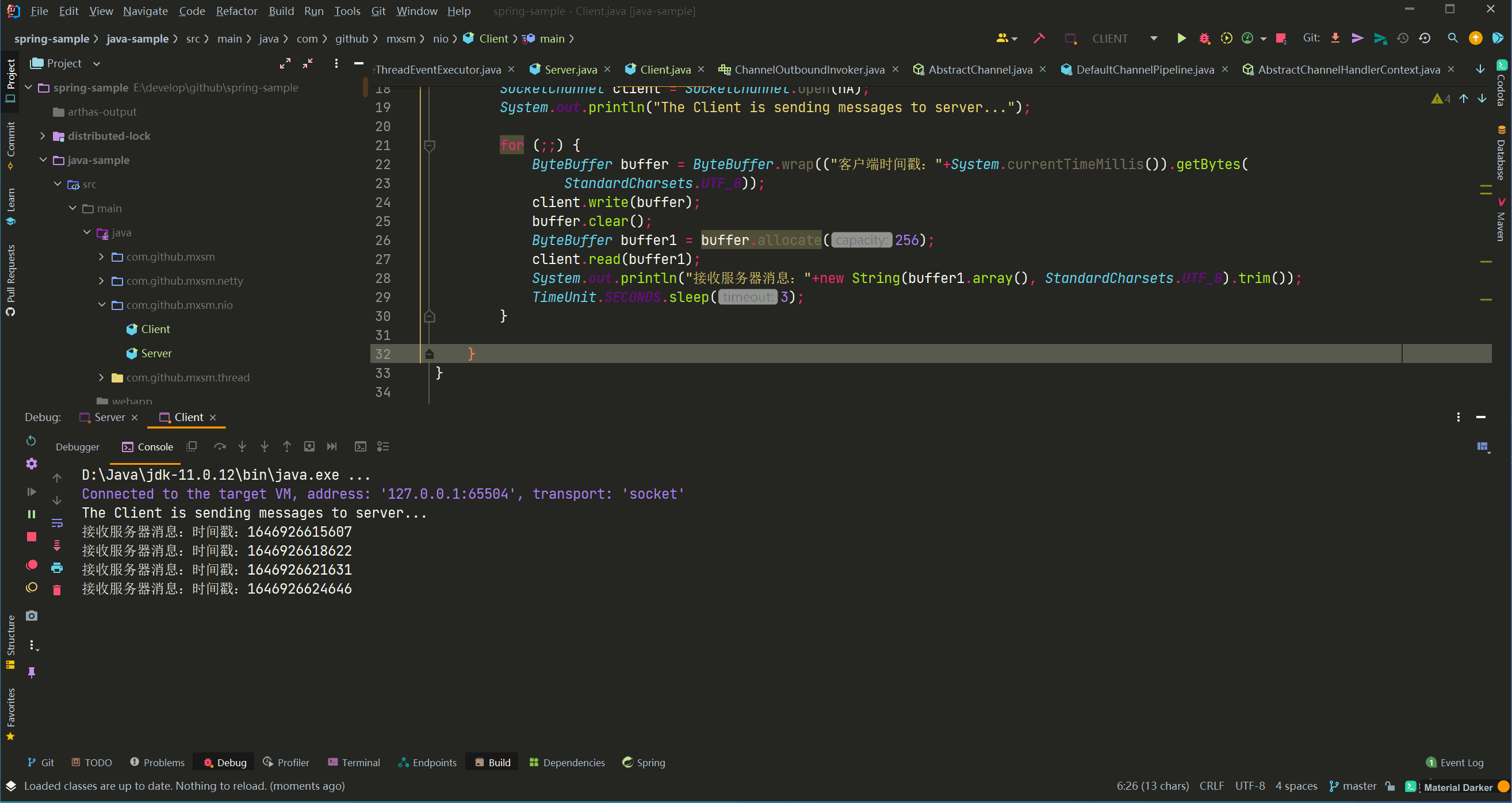
运行结果:
我是蚂蚁背大象,文章对你有帮助点赞关注我,文章有不正确的地方请您斧正留言评论~谢谢