Spring AOP应用之EnableAsync
Spring framework版本 5.3.x
1. 异步核心类
-
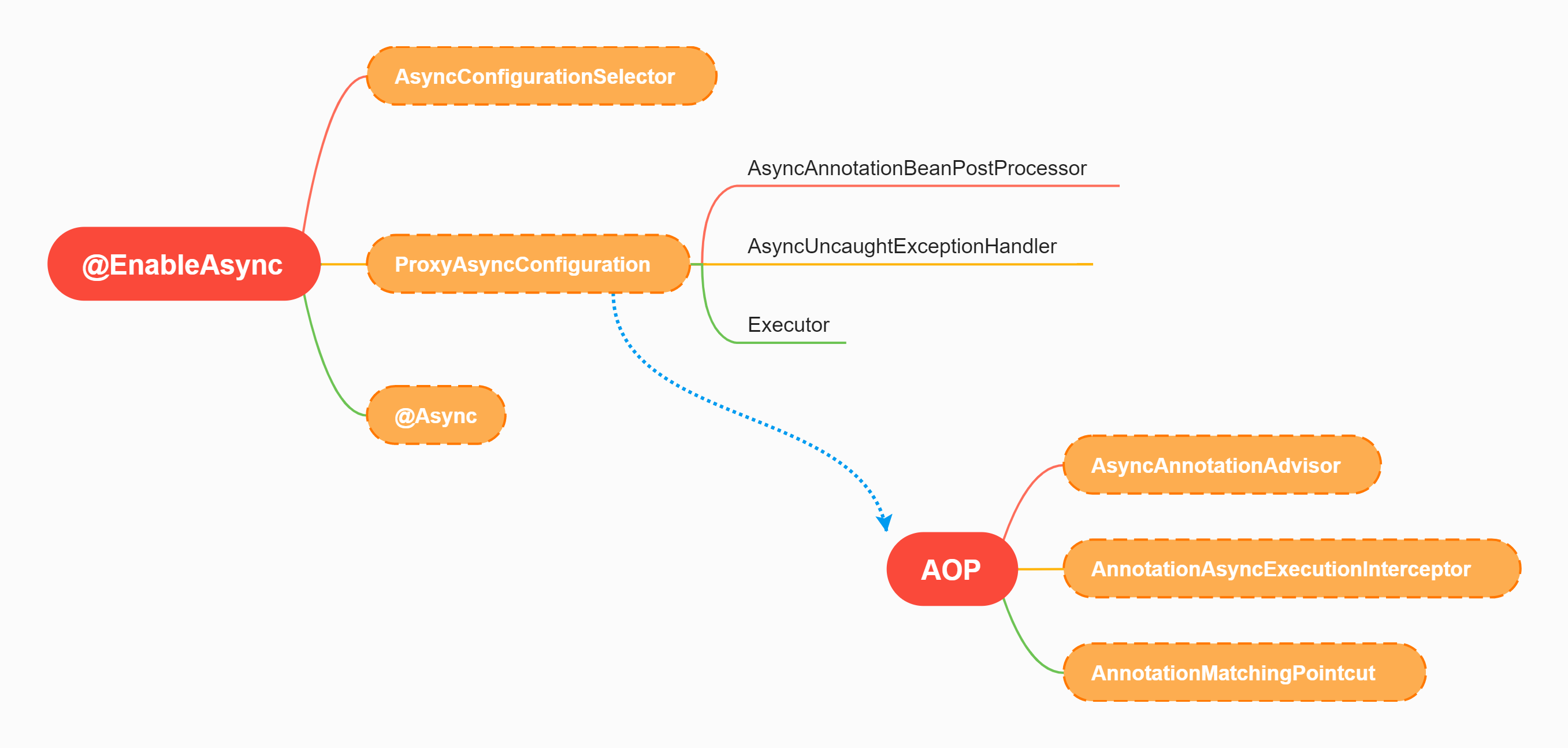
@EnableAsync
开启Spring的异步功能
-
AsyncConfigurationSelector
导入异步功能的配置和处理相关的类
-
ProxyAsyncConfiguration
代理异步配置类,设置了执行线程池、异步错误的处理器,以及AOP相关的三个类
-
AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
处理标记了@Async类和方法(也就是Spring AOP)
-
AOP的三大组件
AsyncAnnotationAdvisor、AnnotationMatchingPointcut、AnnotationAsyncExecutionInterceptor
2. 源码分析
2.1 @EnableAsync源码解析
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Import(AsyncConfigurationSelector.class)
public @interface EnableAsync {
//设置自定义的注解
Class<? extends Annotation> annotation() default Annotation.class;
boolean proxyTargetClass() default false;
AdviceMode mode() default AdviceMode.PROXY;
int order() default Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE;
}
从上面可以看出主要使用了 AsyncConfigurationSelector 来导入选择导入配置类,下面来看一下
2.2 AsyncConfigurationSelector源码解析
public class AsyncConfigurationSelector extends AdviceModeImportSelector<EnableAsync> {
private static final String ASYNC_EXECUTION_ASPECT_CONFIGURATION_CLASS_NAME =
"org.springframework.scheduling.aspectj.AspectJAsyncConfiguration";
@Override
@Nullable
public String[] selectImports(AdviceMode adviceMode) {
switch (adviceMode) {
case PROXY:
return new String[] {ProxyAsyncConfiguration.class.getName()};
case ASPECTJ:
return new String[] {ASYNC_EXECUTION_ASPECT_CONFIGURATION_CLASS_NAME};
default:
return null;
}
}
}
在这里主要导入了配置 ProxyAsyncConfiguration 。这个类主要的作用也是导入配置类。接着来看一下配置类。
2.3 ProxyAsyncConfiguration源码解析
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public class ProxyAsyncConfiguration extends AbstractAsyncConfiguration {
@Bean(name = TaskManagementConfigUtils.ASYNC_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor asyncAdvisor() {
Assert.notNull(this.enableAsync, "@EnableAsync annotation metadata was not injected");
AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor bpp = new AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor();
bpp.configure(this.executor, this.exceptionHandler);
Class<? extends Annotation> customAsyncAnnotation = this.enableAsync.getClass("annotation");
if (customAsyncAnnotation != AnnotationUtils.getDefaultValue(EnableAsync.class, "annotation")) {
bpp.setAsyncAnnotationType(customAsyncAnnotation);
}
bpp.setProxyTargetClass(this.enableAsync.getBoolean("proxyTargetClass"));
bpp.setOrder(this.enableAsync.<Integer>getNumber("order"));
return bpp;
}
}
ProxyAsyncConfiguration 配置继承了 AbstractAsyncConfiguration 。整个主要做了三件事情:
-
ProxyAsyncConfiguration创建了AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor。AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor主要用来实现AOP
-
AbstractAsyncConfiguration主要设置了异步执行的线程池Executor,和执行报错没有捕捉到的错误的处理器 AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler
Executor和AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler可以通过AsyncConfigurer来进行配置。
Tpis: AsyncConfigurer只能配置一个
2.4 AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor源码解析
在类中有这样的一段代码:
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) {
super.setBeanFactory(beanFactory);
AsyncAnnotationAdvisor advisor = new AsyncAnnotationAdvisor(this.executor, this.exceptionHandler);
if (this.asyncAnnotationType != null) {
advisor.setAsyncAnnotationType(this.asyncAnnotationType);
}
advisor.setBeanFactory(beanFactory);
this.advisor = advisor;
}
创建一个 AsyncAnnotationAdvisor 。看一下使用的构造函数:
public class AsyncAnnotationAdvisor extends AbstractPointcutAdvisor implements BeanFactoryAware {
private Advice advice;
private Pointcut pointcut;
//省略了部分代码
public AsyncAnnotationAdvisor(
@Nullable Supplier<Executor> executor, @Nullable Supplier<AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler> exceptionHandler) {
Set<Class<? extends Annotation>> asyncAnnotationTypes = new LinkedHashSet<>(2);
asyncAnnotationTypes.add(Async.class);
try {
asyncAnnotationTypes.add((Class<? extends Annotation>)
ClassUtils.forName("javax.ejb.Asynchronous", AsyncAnnotationAdvisor.class.getClassLoader()));
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// If EJB 3.1 API not present, simply ignore.
}
this.advice = buildAdvice(executor, exceptionHandler);
this.pointcut = buildPointcut(asyncAnnotationTypes);
}
}
从代码可以看出来有两个属性 Advice和Pointcut两个属性加上类本身就是 AOP的三大标准组件。
设置异步Spring定义注解@Async和javax.ejb.Asynchronous注解。
buildAdvice 用来创建 Advice :
protected Advice buildAdvice(
@Nullable Supplier<Executor> executor, @Nullable Supplier<AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler> exceptionHandler) {
AnnotationAsyncExecutionInterceptor interceptor = new AnnotationAsyncExecutionInterceptor(null);
interceptor.configure(executor, exceptionHandler);
return interceptor;
}
buildPointcut 来创建 Pointcut :
protected Pointcut buildPointcut(Set<Class<? extends Annotation>> asyncAnnotationTypes) {
ComposablePointcut result = null;
for (Class<? extends Annotation> asyncAnnotationType : asyncAnnotationTypes) {
//创建类的Pointcut
Pointcut cpc = new AnnotationMatchingPointcut(asyncAnnotationType, true);
//创建方法的Pointcut
Pointcut mpc = new AnnotationMatchingPointcut(null, asyncAnnotationType, true);
if (result == null) {
result = new ComposablePointcut(cpc);
}
else {
result.union(cpc);
}
result = result.union(mpc);
}
return (result != null ? result : Pointcut.TRUE);
}
Pointcut 分成两类:
- @Async放在类上面
- @Async放在方法上面
创建完成 AsyncAnnotationAdvisor 后然后设置自定义的异步注解和创建 Pointcut
public void setAsyncAnnotationType(Class<? extends Annotation> asyncAnnotationType) {
Assert.notNull(asyncAnnotationType, "'asyncAnnotationType' must not be null");
Set<Class<? extends Annotation>> asyncAnnotationTypes = new HashSet<>();
asyncAnnotationTypes.add(asyncAnnotationType);
this.pointcut = buildPointcut(asyncAnnotationTypes);
}
到这里基本上就完成Advisor的创建。下面就是看如何创建代理类。
2.5 AbstractAdvisingBeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInitialization创建代理类
和前面的 @EnableAspectJAutoProxy 注解一样都是通过 postProcessAfterInitialization 方法来实现代理类:
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
if (this.advisor == null || bean instanceof AopInfrastructureBean) {
// Ignore AOP infrastructure such as scoped proxies.
return bean;
}
//判断是否继承了Advised接口
if (bean instanceof Advised) {
Advised advised = (Advised) bean;
if (!advised.isFrozen() && isEligible(AopUtils.getTargetClass(bean))) {
// Add our local Advisor to the existing proxy's Advisor chain...
if (this.beforeExistingAdvisors) {
advised.addAdvisor(0, this.advisor);
}
else {
advised.addAdvisor(this.advisor);
}
return bean;
}
}
//判断是bean是否符合条件
if (isEligible(bean, beanName)) {
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = prepareProxyFactory(bean, beanName);
if (!proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass()) {
evaluateProxyInterfaces(bean.getClass(), proxyFactory);
}
proxyFactory.addAdvisor(this.advisor);
customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory);
// Use original ClassLoader if bean class not locally loaded in overriding class loader
ClassLoader classLoader = getProxyClassLoader();
if (classLoader instanceof SmartClassLoader && classLoader != bean.getClass().getClassLoader()) {
classLoader = ((SmartClassLoader) classLoader).getOriginalClassLoader();
}
return proxyFactory.getProxy(classLoader);
}
// No proxy needed.
return bean;
}
上面有两个判断:
- 判断是否是
Advised的实例如果是并且没有冻结并且符合条件的目标类那么将Advisor添加到 Adviced类 - 如果是符合条件的类(符合条件:被@Async和配置在 @EnableAsync 的 annotation 属性中的注解)
这里就完成代理类生成。
2.6 异步方法如何执行
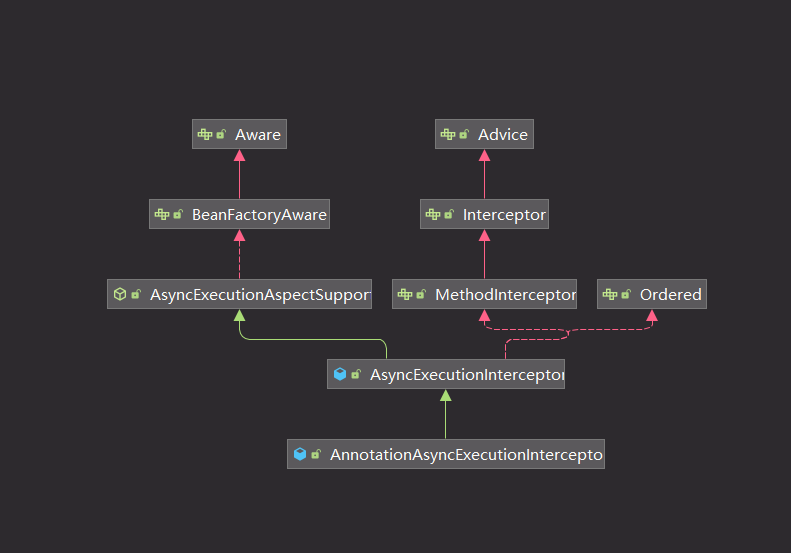
如上图的类关系图,AsyncExecutionInterceptor 实现了 MethodInterceptor#invoke 方法。
下面来看一下这个实现方法的代码(AsyncExecutionInterceptor#invoke):
public Object invoke(final MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
Class<?> targetClass = (invocation.getThis() != null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(invocation.getThis()) : null);
Method specificMethod = ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(invocation.getMethod(), targetClass);
final Method userDeclaredMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(specificMethod);
AsyncTaskExecutor executor = determineAsyncExecutor(userDeclaredMethod);
if (executor == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"No executor specified and no default executor set on AsyncExecutionInterceptor either");
}
Callable<Object> task = () -> {
try {
Object result = invocation.proceed();
if (result instanceof Future) {
return ((Future<?>) result).get();
}
}
catch (ExecutionException ex) {
handleError(ex.getCause(), userDeclaredMethod, invocation.getArguments());
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleError(ex, userDeclaredMethod, invocation.getArguments());
}
return null;
};
return doSubmit(task, executor, invocation.getMethod().getReturnType());
}
从代码可以看出来有这样几个步骤
- 根据执行的方法的具体配置来决定到底使用哪个线程池
- 构建 Callable 任务
- 提交任务给线程执行
3. 总结
对于Spring异步来说,总体的原理还是利用Spring AOP作为基础来实现。