Spring BeanPostProcessor执行顺序问题
Spring Framework版本:5.3.x
BeanPostProcessor 在Spring框架中举足轻重,还有很多继承的类。
作用:管理Bean的生命周期:Bean实例化--->Bean初始化--->Bean使用中--->Bean销毁
在Spring 容器初始化的时候就会存在这些类执行的一个先后的问题,今天我们就把这些类的执行先后顺序进行梳理。
1. BeanPostProcessor的分类
BeanPostProcessor 作为顶层接口会有很多的继承接口和实现类,下图就是分类:
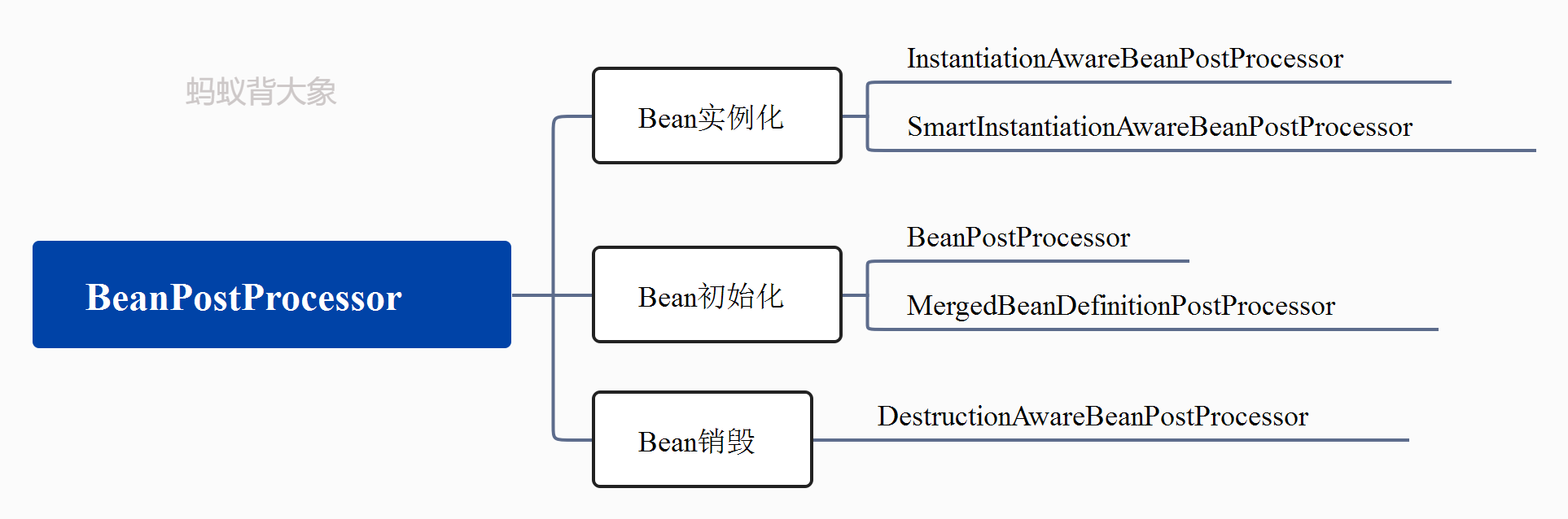
如上图所示包括 BeanPostProcessor 在内,一共有五个接口类。分成了三个功能模块。
- Bean实例化这要由InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor、SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor负责。
- Bean初始化由BeanPostProcessor、MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor两个接口负责
- Bean销毁由DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor接口负责
从分类可以看出来这个五个接口分别对应Bean的三个阶段:实例化、初始化、以及销毁。那么各个阶段里面的执行顺序是怎么样的我们接着往下分析
2. 接口的执行顺序
BeanPostProcessor主要负责Bean的生命周期,那么我们从获取Bean的接口入手看获取到Bean的过程中需要执行那些接口。跟踪代码最终跟踪到了 AbstractBeanFactory#doGetBean方法:
//AbstractBeanFactory#doGetBean
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, () -> {
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
// Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there
// eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution.
// Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean.
destroySingleton(beanName);
throw ex;
}
});
beanInstance = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
在这个当中有一个 createBean 方法。从名称可以知道是用来创建Bean的(实例化)。在这个方法里面主要有三段重要代码:
protected Object doCreateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
//省略部分代码
// Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition.
synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) {
if (!mbd.postProcessed) {
try {
applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Post-processing of merged bean definition failed", ex);
}
mbd.postProcessed = true;
}
}
// Initialize the bean instance.
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) {
throw (BeanCreationException) ex;
}
else {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex);
}
}
// Register bean as disposable.
try {
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex);
}
return exposedObject;
}
这段代码涵盖了上面五个接口的四个分别是:InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor、SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor、BeanPostProcessor、MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor。唯一的Bean的销毁,Bean的销毁是随着Spring容器销毁而销毁的。整个执行的流程和步骤如下图:
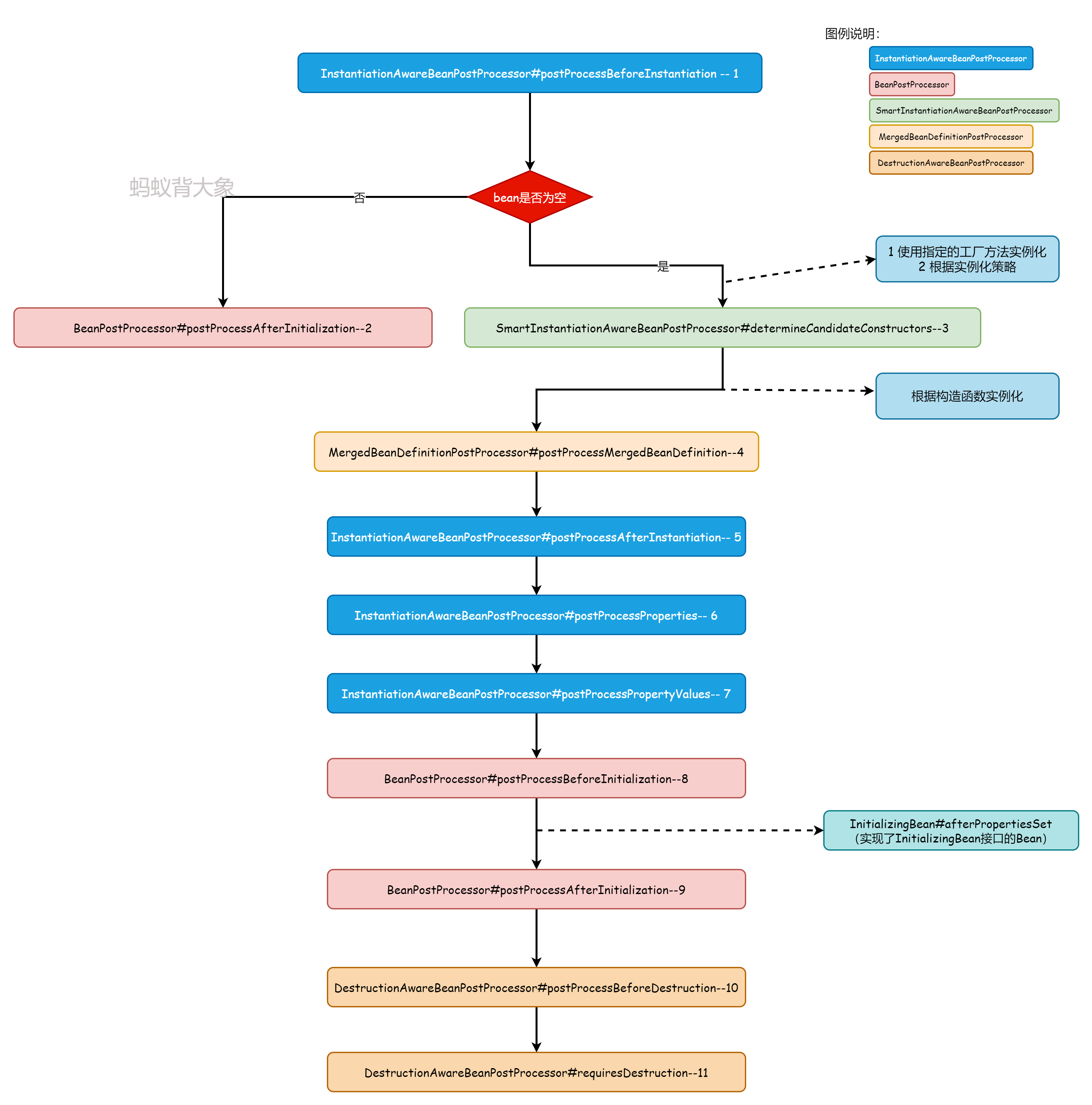
从上图的执行顺序可以看出来:
- 接口之间的执行顺序不�是严格按照: 实例化->初始化->销毁 这样的严格顺序来进行。接口方法之间的顺序会有穿插的情况。
- InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation 方法执行如果返回了对应的Bean的实例,后续的接口都不会执行了。
这里我们可以加入自定义的类。典型的例子就是动态代理的实现,可以继承当前接口并且在改方法中实现动态代理。这样在Spring 容器中的实例就是一个动态代理实例。 - DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor 接口一般情况下是不会执行,只有当Spring容器销毁就会触发容器里面类的销毁机制。
- 同一种类型接口如果有继承 PriorityOrdered 和Ordered进行排序。
Tips: 对于基于BeanPostProcessor自定义开发来说,主要用于自定义方法或者属性类上面的注解。这里举两个Spring的例子:AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 处理@Autowired, @Value注解, AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 处理 @Async注解。这些注解都是在属性上或者方法上面。
3. 总结
- BeanPostProcessor 接口主要是启动的时候添加到Spring容器中提供给后续的使用
- BeanPostProcessor 接口执行主要发生在获取Bean的流程中(Bean的生命周期)
- 自定义开发可以参照Spring已有的实现,能够更加明了的知道如何进行进一步拓展使用