深入了解WebApplicationInitializer是消除web.xml和springMVC的配置文件
1. Servlet3.x规范一些知识
1.1 java Servlet3.x的相关规范
可以参看:Servlet相关笔记
在Servlet的规范中有两种方式来实现 ServletContext 的初始化,通过XML的配置文件或者通过编程的方式来进行初始化。
注解和XML都是可拔插的组件,通过不同的方式来实现不同需求,
ServletContainerInitializer 类通过 jar services API 查找。对于每一个应用,应用启动时,由容器创建一个ServletContainerInitializer 实例。 框架提供的 ServletContainerInitializer 实现必须绑定在 jar 包 的 META-INF/services 目录中的一个叫做 javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer 的文件,根据 jar services API,指定 ServletContainerInitializer 的实现。除 ServletContainerInitializer 外,我们还有一个注解—HandlesTypes。在 ServletContainerInitializer 实现上的 HandlesTypes 注解用于表示感兴趣的一些类,它们可能指定了 HandlesTypes 的 value 中的注解(类型、方法或自动级别的注解),或者是其类型的超类继承/实现了这些类之一。无论是否设置了 metadata-complete,HandlesTypes 注解将应用。当检测一个应用的类看是否它们匹配 ServletContainerInitializer 的 HandlesTypes 指定的条件时,如果应用的一个或多个可选的 JAR 包缺失,容器可能遇到类装载问题。由于容器不能决定是否这些类型的类装载失败 将阻止应用正常工作,它必须忽略它们,同时也提供一个将记录它们的配置选项。 如果 ServletContainerInitializer 实现没有@HandlesTypes注解,或如果没有匹配任何指定的 HandlesType,那 么它会为每个应用使用 null 值的集合调用一次。这将允许 initializer 基于应用中可用的资源决定是否需要初始化 Servlet/Filter。在任何 Servlet Listener 的事件被触发之前,当应用正在启动时,ServletContainerInitializer 的 onStartup 方法将被调用。ServletContainerInitializer’s 的 onStartup 得到一个类的Set,其或者继承/实现 initializer 表示感兴趣的类,或者它是使用指定在@HandlesTypes 注解中的任意类注解的。
2. SpringServletContainerInitializer介绍
@HandlesTypes(WebApplicationInitializer.class)
public class SpringServletContainerInitializer implements ServletContainerInitializer {
@Override
public void onStartup(@Nullable Set<Class<?>> webAppInitializerClasses, ServletContext servletContext)
throws ServletException {
List<WebApplicationInitializer> initializers = new LinkedList<>();
if (webAppInitializerClasses != null) {
for (Class<?> waiClass : webAppInitializerClasses) {
// Be defensive: Some servlet containers provide us with invalid classes,
// no matter what @HandlesTypes says...
if (!waiClass.isInterface() && !Modifier.isAbstract(waiClass.getModifiers()) &&
WebApplicationInitializer.class.isAssignableFrom(waiClass)) {
try {
initializers.add((WebApplicationInitializer)
ReflectionUtils.accessibleConstructor(waiClass).newInstance());
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ServletException("Failed to instantiate WebApplicationInitializer class", ex);
}
}
}
}
if (initializers.isEmpty()) {
//打印日志
return;
}
//打印日志
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(initializers);
for (WebApplicationInitializer initializer : initializers) {
//调用WebApplicationInitializer的方法onStartup
initializer.onStartup(servletContext);
}
}
}
SpringServletContainerInitializer 继承了 ServletContainerInitializer 在对应的jar包下面的 META-INF.services 下面有一个文件 javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer 内容如下:
org.springframework.web.SpringServletContainerInitializer
通过SPI就能加载 SpringServletContainerInitializer 类,然后通过定义在上面的 @HandlesTypes 注解。根据配置的类 WebApplicationInitializer 来加载。通过 WebApplicationInitializer 来把Servlet和Spring结合起来。
3. WebApplicationInitializer介绍
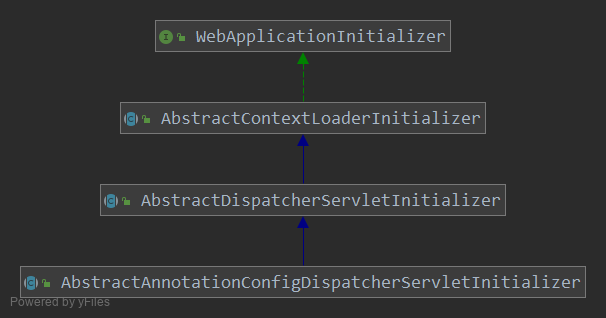
从上面可以看出来 WebApplicationInitializer 有三个继承实现类,三个抽象的类单一继承。下面分析一下下面的几个初始化类:
-
WebApplicationInitializer
public interface WebApplicationInitializer {
//启动方法
void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException;
}在 WebApplicationInitializer 中只有一个方法,在 SpringServletContainerInitializer 类中调用了这个
onStartup方法。 -
AbstractContextLoaderInitializer
public abstract class AbstractContextLoaderInitializer implements WebApplicationInitializer {
/** Logger available to subclasses. */
protected final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
@Override
public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
registerContextLoaderListener(servletContext);
}
//添加ContextLoaderListener到ServletContext
protected void registerContextLoaderListener(ServletContext servletContext) {
WebApplicationContext rootAppContext = createRootApplicationContext();
if (rootAppContext != null) {
ContextLoaderListener listener = new ContextLoaderListener(rootAppContext);
listener.setContextInitializers(getRootApplicationContextInitializers());
servletContext.addListener(listener);
}
else {
//打印日志
}
}
//创建Spring的WebApplicationContext
@Nullable
protected abstract WebApplicationContext createRootApplicationContext();
@Nullable
protected ApplicationContextInitializer<?>[] getRootApplicationContextInitializers() {
return null;
}
} -
AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer
public abstract class AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer extends AbstractContextLoaderInitializer {
//默认的Servlet名称
public static final String DEFAULT_SERVLET_NAME = "dispatcher";
@Override
public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
super.onStartup(servletContext);
//注册DispatcherServlet
registerDispatcherServlet(servletContext);
}
//注册注册DispatcherServlet的方法
protected void registerDispatcherServlet(ServletContext servletContext) {
String servletName = getServletName();
Assert.hasLength(servletName, "getServletName() must not return null or empty");
//抽象方法createServletApplicationContext由使用者自己实现
WebApplicationContext servletAppContext = createServletApplicationContext();
Assert.notNull(servletAppContext, "createServletApplicationContext() must not return null");
FrameworkServlet dispatcherServlet = createDispatcherServlet(servletAppContext);
Assert.notNull(dispatcherServlet, "createDispatcherServlet(WebApplicationContext) must not return null");
dispatcherServlet.setContextInitializers(getServletApplicationContextInitializers());
ServletRegistration.Dynamic registration = servletContext.addServlet(servletName, dispatcherServlet);
if (registration == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to register servlet with name '" + servletName + "'. " +
"Check if there is another servlet registered under the same name.");
}
registration.setLoadOnStartup(1);
registration.addMapping(getServletMappings());
registration.setAsyncSupported(isAsyncSupported());
Filter[] filters = getServletFilters();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(filters)) {
for (Filter filter : filters) {
registerServletFilter(servletContext, filter);
}
}
customizeRegistration(registration);
}
/**
* Return the name under which the {@link DispatcherServlet} will be registered.
* Defaults to {@link #DEFAULT_SERVLET_NAME}.
* @see #registerDispatcherServlet(ServletContext)
*/
protected String getServletName() {
return DEFAULT_SERVLET_NAME;
}
/**
* Create a servlet application context to be provided to the {@code DispatcherServlet}.
* <p>The returned context is delegated to Spring's
* {@link DispatcherServlet#DispatcherServlet(WebApplicationContext)}. As such,
* it typically contains controllers, view resolvers, locale resolvers, and other
* web-related beans.
* @see #registerDispatcherServlet(ServletContext)
*/
protected abstract WebApplicationContext createServletApplicationContext();
/**
* Create a {@link DispatcherServlet} (or other kind of {@link FrameworkServlet}-derived
* dispatcher) with the specified {@link WebApplicationContext}.
* <p>Note: This allows for any {@link FrameworkServlet} subclass as of 4.2.3.
* Previously, it insisted on returning a {@link DispatcherServlet} or subclass thereof.
*/
protected FrameworkServlet createDispatcherServlet(WebApplicationContext servletAppContext) {
return new DispatcherServlet(servletAppContext);
}
/**
* Specify application context initializers to be applied to the servlet-specific
* application context that the {@code DispatcherServlet} is being created with.
* @since 4.2
* @see #createServletApplicationContext()
* @see DispatcherServlet#setContextInitializers
* @see #getRootApplicationContextInitializers()
*/
@Nullable
protected ApplicationContextInitializer<?>[] getServletApplicationContextInitializers() {
return null;
}
/**
* Specify the servlet mapping(s) for the {@code DispatcherServlet} —
* for example {@code "/"}, {@code "/app"}, etc.
* @see #registerDispatcherServlet(ServletContext)
*/
protected abstract String[] getServletMappings();
/**
* Specify filters to add and map to the {@code DispatcherServlet}.
* @return an array of filters or {@code null}
* @see #registerServletFilter(ServletContext, Filter)
*/
@Nullable
protected Filter[] getServletFilters() {
return null;
}
/**
* Add the given filter to the ServletContext and map it to the
* {@code DispatcherServlet} as follows:
* <ul>
* <li>a default filter name is chosen based on its concrete type
* <li>the {@code asyncSupported} flag is set depending on the
* return value of {@link #isAsyncSupported() asyncSupported}
* <li>a filter mapping is created with dispatcher types {@code REQUEST},
* {@code FORWARD}, {@code INCLUDE}, and conditionally {@code ASYNC} depending
* on the return value of {@link #isAsyncSupported() asyncSupported}
* </ul>
* <p>If the above defaults are not suitable or insufficient, override this
* method and register filters directly with the {@code ServletContext}.
* @param servletContext the servlet context to register filters with
* @param filter the filter to be registered
* @return the filter registration
*/
protected FilterRegistration.Dynamic registerServletFilter(ServletContext servletContext, Filter filter) {
String filterName = Conventions.getVariableName(filter);
Dynamic registration = servletContext.addFilter(filterName, filter);
if (registration == null) {
int counter = 0;
while (registration == null) {
if (counter == 100) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to register filter with name '" + filterName + "'. " +
"Check if there is another filter registered under the same name.");
}
registration = servletContext.addFilter(filterName + "#" + counter, filter);
counter++;
}
}
registration.setAsyncSupported(isAsyncSupported());
registration.addMappingForServletNames(getDispatcherTypes(), false, getServletName());
return registration;
}
private EnumSet<DispatcherType> getDispatcherTypes() {
return (isAsyncSupported() ?
EnumSet.of(DispatcherType.REQUEST, DispatcherType.FORWARD, DispatcherType.INCLUDE, DispatcherType.ASYNC) :
EnumSet.of(DispatcherType.REQUEST, DispatcherType.FORWARD, DispatcherType.INCLUDE));
}
/**
* A single place to control the {@code asyncSupported} flag for the
* {@code DispatcherServlet} and all filters added via {@link #getServletFilters()}.
* <p>The default value is "true".
*/
protected boolean isAsyncSupported() {
return true;
}
/**
* Optionally perform further registration customization once
* {@link #registerDispatcherServlet(ServletContext)} has completed.
* @param registration the {@code DispatcherServlet} registration to be customized
* @see #registerDispatcherServlet(ServletContext)
*/
protected void customizeRegistration(ServletRegistration.Dynamic registration) {
}
} -
AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer